food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome and allergic proctocolitis
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome and Proctocolitis. Symptoms usually start at one to four weeks of age and range from having blood which is sometimes seen with mucous in bowel movements to blood stained loose stools or.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Semantic Scholar
8 hours agoType 1 food allergy signssymptoms usually start.

. FPIAP prevalence estimates range widely from 016 in healthy children and 64 in patients with blood in stools. Educational clinical case series for pediatric allergy and immunology. All three are typically present in infancy and are triggered most commonly by cows milk protein.
It often presents as rectal bleeding in an otherwise healthy young infant although other infants may have significant irritability and diarrhea 1. A greater likelihood may exist of a. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES allergic proctocolitis FPIAP and enteropathy FPE are among a.
Cows milk protein allergy is the most common food allergy in infants and young children. Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP is a condition characterized by inflammatory changes in the distal colon in response to one or more foreign food proteins because of immune-mediated reactions. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is caused by an allergic reaction to one or more ingested foods which results in inflammation of the small and large intestine.
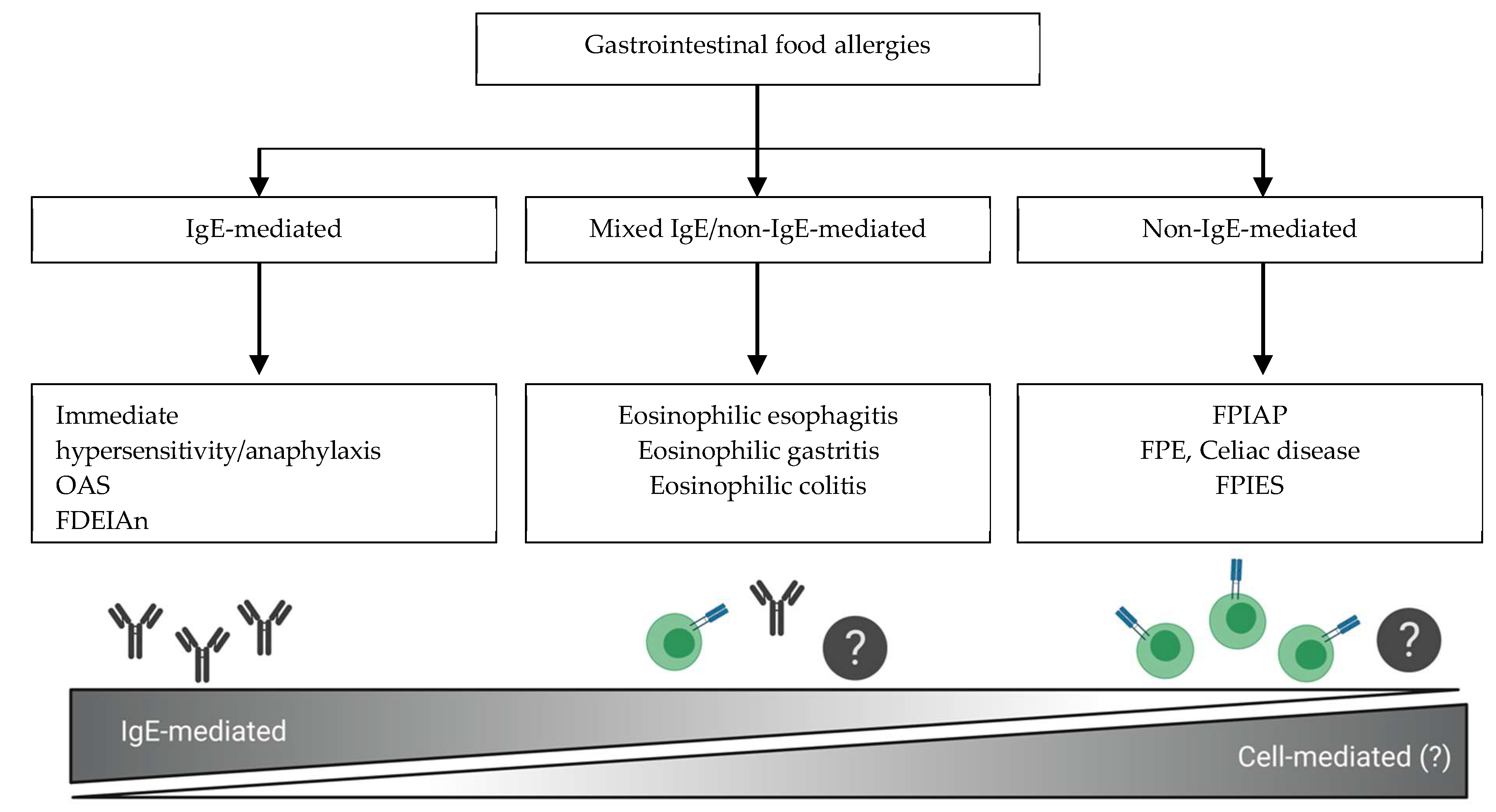
Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating. Food proteineinduced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP is a benign self-limited disorder that affects young infants within the first few months of life. Non-IgE cell-mediated food allergic disorders encompass food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP food protein-induced enteropathy Heiners syndrome pulmonary hemosiderosis celiac disease and cows milk CM protein-induced iron deficiency anemia.
Up to 10 cash back Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Allergic Proctocolitis and Enteropathy Abstract. We aim to review the recent literature and to provide an update on diagnosis and management of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES and food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP. It has been recently reported that FPIPC is a rare cause of rectal bleeding in newborns and most cases have been proved to be due to idiopathic neonatal transient colitis.
Characteristics of children with food protein-induced enterocolitis and allergic proctocolitis. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon.
Formerly known as allergic or eosinophilic proctocolitis or protein intolerance is a common problem in young infants. FPIES manifests in infants as profuse repetitive vomiting and lethargy often with diarrhea leading to. Non-IgE-mediated food allergic disorders account for up to 40 of milk protein allergy in infants and young children.
Non-IgE-mediated food allergy encompasses a wide range of disorders affecting. Cows milk is the most common trigger of both FPIAP and FPIES. A similar syndrome in adults has been associated primarily with.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a form of non-IgE mediated gastrointestinal food allergy. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy primarily diagnosed in infancy but has also been reported in older children and adults. The only known cause is food protein-induced proctocolitis FPIPC.
1 In 1967 one of the first case descriptions of FPIES by Gryboski described 21 hospitalized patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal milk allergy that presented with symptoms of chronic diarrhea and. Food proteininduced enterocolitis syndrome allergic proctocolitis. 12 Because celiac disease is traditionally managed by.
The symptom onset age seemed to be earlier in FPIAP. Written in collaboration by. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated food allergy that usually occurs in young infants 1.
Careful elimination and food journaling has identified reaction loose mucosy bloody stools to cows milk soy wheat and egg. Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis FPIAP Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP is a type of delayed inflammatory non-IgE mediated gut food allergy. 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21.
Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy non-IgE-GI-FA is the name given to a series of pathologies whose main entities are food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP food protein-induced enteropathy FPE and food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an adverse food reaction involving the immune system that mainly affects infants and young children. Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP is a type of delayed inflammatory non-IgE mediated gut food allergy.
Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Infants with FPIAP are usually otherwise healthy and growing well. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that affects the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Allergic proctocolitis food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome and allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis with protein-losing gastroenteropathy as manifestations of non-IgE-mediated cows milk allergy. We aim to review the recent literature and to provide an update on diagnosis. Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP.
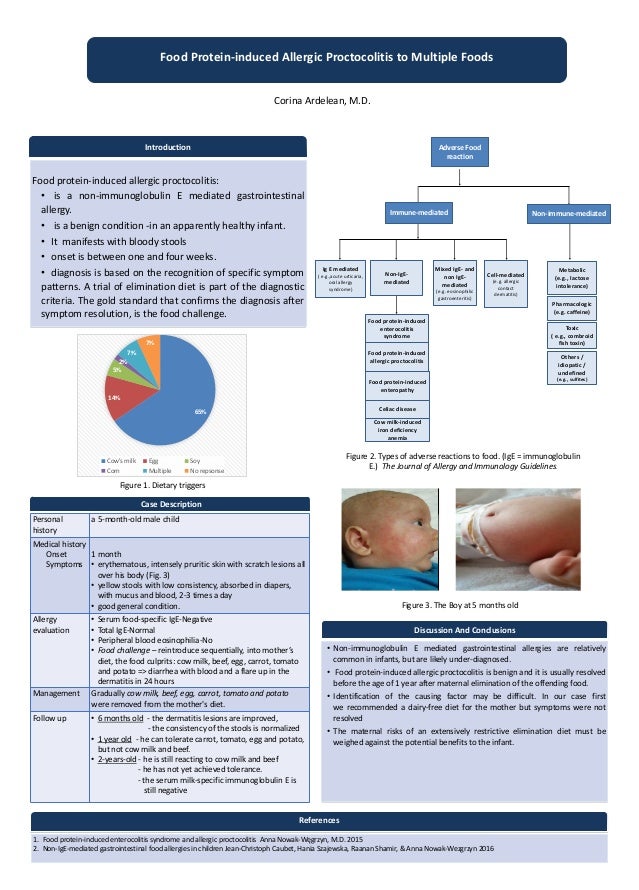
Non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergic disorders non-IgE-GI-FA include food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES food protein-induced enteropathy FPE and food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP which present with symptoms of variable severity affecting the gastrointestinal tract in response to specific dietary antigens. I have a 3 month-old male breastfed patient with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome and allergic proctocolitis FPIAP to multiple foods and normal growthdevelopment. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES allergic proctocolitis FPIAP and enteropathy FPE are among a number of immune-mediated reactions to food that are thought to occur primarily via non-IgE-mediated pathways.
Symptoms usually start at one to four weeks of age and range from having blood which is sometimes seen with mucous in bowel movements to blood stained loose stools or diarrhoea. The etiology of small and fresh rectal bleeding in neonates who are not sick is usually unknown. The peer-reviewed articles indexed in PubMed have been reviewed.
The resolution age was similar however the recovery in FPIES may be later if the trigger food is solid.
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Pdf Gastrointestinal Food Allergy In Infants Semantic Scholar
Food Protein Induced Allergic Proctocolitis To Multiple Foods
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Allergic Proctocolitis In Infants Literature Review And Proposal Of A Management Protocol World Allergy Organization Journal

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Dr Costa Private Children S Allergy Clinic

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Semantic Scholar

Description Of Differences And Similarities Between Fpies Fpe And Download Scientific Diagram

Advances In Understanding Immune Mechanisms Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

References In Immunopathophysiology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Semantic Scholar

A Slice Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Insights From 441 Children With Fpies As Provided By Caregivers In The International Fpies Association The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table